| Did you know that over a quarter of the worlds population is myopic? Myopia is simply a condition where the object being viewed front of the retina, thus creating a blurred image on the retina. | 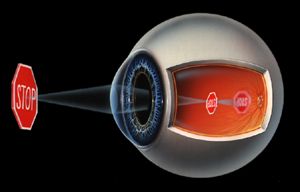 |
| Did you know that over a quarter of the worlds population is myopic? Myopia is simply a condition where the object being viewed front of the retina, thus creating a blurred image on the retina. |  |
| With this condition, the image is not coming into focus on the retina, but "behind" the retina. Therefore, when the image reaches the retina, it is still in a blurry form. How far behind the retina the image would come into focus depends on the amount of farsightedness one has. What causes the eye to be hyperopic or farsighted? If the cornea is too flat and therefore not strong enough, or if the eye has a shorter than average axial length, the image is going to come into focus "behind" the retina. Using the camera analogy: The optical system of the camera, our eye, is failing to make the picture come into focus on the film, our retina. Unlike myopia, an eye with this refractive condition usually is stable before the age of twenty. | 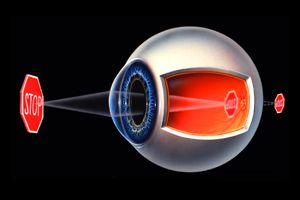 |
A condition
in which the lens of your eye loses flexibility making
it difficult to focus on close objects. It is natural to lose enough
flexibility by the mid 40's to become noticeable to the individual..
| Astigmatism means that the front of the eye, the cornea, is not symmetrical or spherical. A cornea without astigmatism is shaped like a basketball. A cornea with astigmatism is shaped more like a football, with two different curvatures, one steeper than the other. | 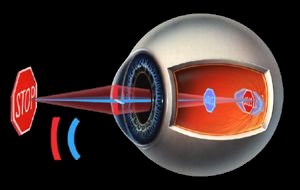 |
The pupil is the small opening in the eye that light passes through to eventually reach the retina.
The iris works just like that of a camera expanding and constricting to allow more or less light to reach the retina.
The anterior
chamber is the area between the
iris and the cornea filled with a clear aqueous fluid.
This condition
is a misalignment of the eyes. One or both eyes may turn in, up, out, or
down. Treatment may include prismatic glasses, contacts, visual therapy,
and in some cases surgery.
Reduced visual acuity in an eye that can not be fully corrected with lenses. Amblyopia is typically detected during childhood, and is generally treated by a pediatric vision specialist.
Color blindness is actually a misnomer. The term "color deficiency" is more appropriate. Color deficiency is the inability to distinguish various color groupings. About 1 in 8 men is color deficient as opposed to 1 in 200 women.
Conjunctivitis is a general term for any inflamation of the front of the eye. Commonly known as "pink eye", this condition should be evaluated by our office for treatment.
A condition
caused by the increase of aqueous fluid in the eye resulting in increased
intraocular pressure that causes damage to the optic nerve. Symptoms
may include tunnel vision, pain, blurred vision, halos around lights...
or no signs at all. Glaucoma occurs most commonly in people
over 40 and may result in blindness
if not diagnosed
and treated early in the course of the disease.
Changes to an area of the retina called the macula at the back of the eye resulting in a gradual loss of central vision. Objects appear distorted, color vision weakens, and a dark area appears at the center.
The separation of the retina from the pigment caused by holes or tears in the retina, by a tumor, or by fluid pressure in the area. It can be surgically treated. Aside from a sudden loss of vision, warning signs might include light flashes or unusual spots or floaters.
Small particles of protein or other matter of various size and shape that float within the eye. They appear to dart away when you try and focus on them. Most spots are not harmful and rarely inhibit vision. However, spots may be indicative of more serious problems. You should consult your optometrist if you notice them often, or a sudden increase.
A cataract is a clouding that develops in the normally clear lens of the eye. this prevents the lens from properly focusing light on the retina. Cataracts usually develop in both eyes, but often at different rates. Some some cataracts develop over a period of years, while others form rapidly in a few months.